最近在面试时发现好多人都喜欢在简历中添加“熟悉各种设计模式”那一项。但也不乏对于最为简单的单例,也仅限于书本上的一点认知,所以扯一扯php中单例模式的几种使用场景。
何为单例模式
单例模式属于创建型的应用模式,可以确保某一个类只有一个实例。这在获取数据库,缓存服务器的连接句柄,以及获取配置信息方面非常方便。
使用单例模式,可以减少在一次web请求中多次连接数据库或者解析配置文件等操作对系统资源的消耗,也可以避免大量的new操作。
其UML结构图如下:
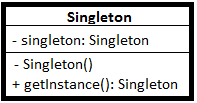
在php中实现单例模式需要注意:
- 需要一个静态变量保存实例
- 需要提供一个公共的静态方法,用于返回需要获取的实例
- 需要防止外部程序通过new和clone等操作产生相关实例,从而失去单例模式的意义
代码实现解析
一个单例模式的php实现大致如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class Singleton
{
private static $_instance = null;
private function __construct()
{
}
public function __clone()
{
trigger_error("clone method is not allowed.", E_USER_ERROR);
}
public static function getInstance()
{
if (self::$_instance === null) {
self::$_instance = new self();
}
return self::$_instance;
}
}
|
上述代码通过静态成员变量保存创建的实例,通过将构造函数设置为私有的,并使用魔术方法__clone“重载”clone方法以避免通过外部程序获取相关实例。
由于php中的静态变量包括:静态全局变量,静态局部变量,静态成员变量,所以也可以通过静态局部变量来保存创建的实例。但是在子类中获取创建的实例时,会遇到一些问题。示例如下:
使用静态局部变量
singleton-static.php1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| class Singleton
{
private $_handle = null;
private function __construct()
{
$this->_handle = new StdClass();
}
public function __clone()
{
trigger_error("clone method is not allowed.", E_USER_ERROR);
}
public static function getInstance()
{
static $_instance = null;
if ($_instance === null) {
$_instance = new self();
}
return $_instance;
}
public function getObj()
{
return $this->_handle;
}
}
class UserModel extends Singleton
{
public static function getUser()
{
var_dump(self::getInstance()->getObj());
}
}
class GroupModel extends Singleton
{
public static function getGroup()
{
var_dump(self::getInstance()->getObj());
}
}
UserModel::getUser();
GroupModel::getGroup();
|
$ php /.singleton-static.php
object(Singleton)#2 (0) {
}
object(Singleton)#4 (0) {
}
此例没有获取到唯一实例,因为局部静态变量,也就是在函数中定义的静态变量。其信息是存储在zend vm为每个函数分配的一个私有符号表中。
php中当继承发生时,会进行函数的合并。UserModel中调用的,实际上是合并在UserModel中的getInstance,GroupModel中调用的,也是合并在GroupModel中的getInstance方法。
因为是在两个不同方法的私有符号表中获取数据,所以取到的不是同一个实例。
可以将self换成parent试试
使用静态成员变量
singleton-static-member.php1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| class Singleton
{
private $_handle = null;
private static $_instance = null;
private function __construct()
{
$this->_handle = new StdClass();
}
public function __clone()
{
trigger_error("clone method is not allowed.", E_USER_ERROR);
}
public static function getInstance()
{
if (self::$_instance === null) {
self::$_instance = new self();
}
return self::$_instance;
}
public function getObj()
{
return $this->_handle;
}
}
class UserModel extends Singleton
{
public static function getUser()
{
var_dump(self::getInstance()->getObj());
}
}
class GroupModel extends Singleton
{
public static function getGroup()
{
var_dump(self::getInstance()->getObj());
}
}
UserModel::getUser();
GroupModel::getGroup();
|
$ php /.singleton-static-member.php
object(Singleton)#2 (0) {
}
object(Singleton)#2 (0) {
}
此时获取到了唯一实例,因为静态成员变量的信息是存储在类结构的 default_static_members 字段,为所有实例所共用。
编写一个单例的基类
有时我们的项目中有个缓存类,还有数据库类,还有个文件操作类。想让这三个类都是单例的话,我们需要实现三个单例,这有点繁琐。于是我们可以创建一个单例的基类,要实现单例的类继承这个基类即可。直接上代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| <?php
class Singleton
{
private static $_instances = array();
protected function __construct()
{
}
final public function __clone()
{
trigger_error("clone method is not allowed.", E_USER_ERROR);
}
final public static function getInstance()
{
$c = get_called_class();
if(!isset(self::$_instances[$c])) {
self::$_instances[$c] = new $c;
}
return self::$_instances[$c];
}
}
class Cache Extends Singleton
{
private $_handle = null;
protected function __construct()
{
$this->_connect();
}
private function _connect()
{
$this->_handle = new StdClass();
}
public function getHandle()
{
return $this->_handle;
}
}
class Db Extends Singleton
{
private $_handle = null;
protected function __construct()
{
$this->_connect();
}
private function _connect()
{
$this->_handle = new StdClass();
}
public function getHandle()
{
return $this->_handle;
}
}
|
reference:
[^1] http://www.php-internals.com/book/?p=chapt05/05-04-class-inherit-abstract
[^2] http://zh.wikipedia.org/zh/%E5%8D%95%E4%BE%8B%E6%A8%A1%E5%BC%8F
[^3] http://www.phptherightway.com/pages/Design-Patterns.html
[^4] http://rancoud.com/read-phps-opcode/
